What is the Purpose of Motherboard Audio Ports?
Sound from a computer is important to users as well as technicians. While users use sound to listen to music or record it, technicians use it to identify the problem. On most personal computers, a special audio circuit generates the sound. If you dial the time back to a couple of decades ago, PCs at the time had dedicated expansion boards known as “Sound Cards”. These cards contain all the audio circuitry that the computer needs to produce the sound. But most modern PCs have the “audio” circuit built right into the motherboard. The job of these dedicated sound cards or integrated audio circuits is to generate the electrical signals that are responsible to produce sound. This is where motherboard audio ports come into the picture. The electrical signals from the audio circuitry terminate at the audio ports (either on the motherboard or on the sound card). We can connect speakers, headphones, etc. to these audio ports and hear the audio. You can find audio ports on the front as well as the rear of a personal computer.
Different Types of Motherboard Audio Ports
An understanding of different types of Motherboard Audio Ports is very important to set up your sound system. The four common types of Audio Ports on a modern motherboard are:
3.5mm Audio Jacks Optical S/PDIF Port Coaxial S/PDIF Port 6.35mm Audio Jack
Let us see more details about these three audio ports on a typical motherboard.
3.5mm Audio Jacks
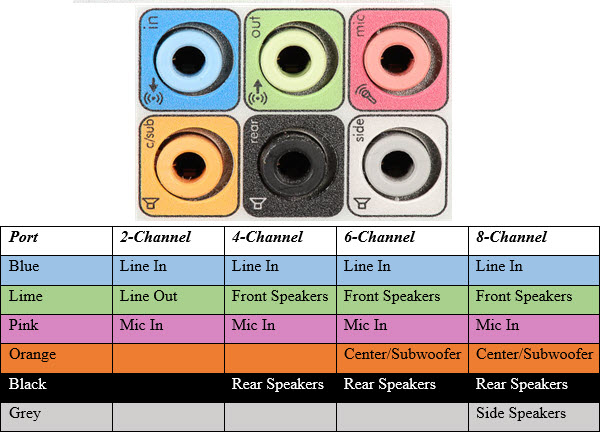
One of the popular and most common types of motherboard audio ports is the 3.5mm jack. We use them to connect headphones as speakers. These ports accept the widely popular 3.5mm TRS Audio Connector. Most motherboards have at least three 3.5mm jacks in the colors Green, Blue, and Pink. In this, the Green 3.5mm Audio Port is known as the Line Out Port. This is the main audio port for connecting two-channel (stereo) headphones or speakers using a 3.5mm Audio Cable. The Blue 3.5mm Audio Port is known as Line In. We use this port to connect external audio equipment such as CD Players, Amplifiers, Certain Musical Instruments, Audio Mixers, Microphones, etc. to the computer. We basically use this port to connect audio sources to the PC. The last “basic” port on a motherboard is the Pink 3.5mm Audio Port. It is known as Mic In, which is short for Microphone In. As the name suggests, we use this port to connect microphones to the computer. Even though the Line In Port accepts a Microphone, the amplification level of the actual Mic In Port or the Pink Port is much better While these are the three basic 3.5mm Audio Ports, some motherboards have up to three additional ports, making it a total of six 3.5mm Audio Ports. These three additional ports allow you to set up a surround sound system. The color codes of these ports are Orange, Black, and Gray. The Orange 3.5mm Audio Ports is known as CS OUT or C/Sub Port. In a surround sound setup, the center channel acts as the main vocal channel and a sub-woofer produces that tight and punchy low-frequency bass audio. We use this Orange Port to connect to the center channel as well as the sub-woofer speakers. Next, we have the Black 3.5mm Audio Port. It is known as RS OUT or simply Rear. In your surround sound system, you have to connect the rear speakers to this port. Finally, we have the Gray 3.5mm Audio Port. This port is useful if you are setting up a 7.1 channel surround sound system. In such a system, there will be two side channels and we connect these speakers to the Gray port. The following image shows the six 3.5mm Audio Ports on a modern motherboard along with their color codes and speaker configurations.
Some computers have front audio and the ports are Green and Pink. So, you can connect your speakers or headphones as well as a microphone in the front itself.
S/PDIF Port
The 3.5mm Audio Jacks we saw earlier generate analog audio signals. But with the growing popularity of digital audio, Sony and Phillips developed a new digital audio protocol known as the Sony Phillips Digital Interface or S/PDIF. Using S/PDIF, you can transmit multi-channel audio through a single cable. Speaking of cable, there are two popular physical media that carry S/PDIF signals. They are Optical and Coaxial. The Optical S/PDIF uses a TOSLINK, which is short for Toshiba Link, connector, and an optical fiber medium. On the other hand, the coaxial S/PDIF uses a coaxial cable and an RCA Connector. As it can carry compressed 5.1 DTS or Dolby Digital Audio, the S/PDIF Port is suitable if you are setting a surround sound system with the help of a single cable.
6.35mm Audio Jack
It is very rare but some motherboards have a 6.35mm Audio Jack. This jack is suitable if you have a high-quality home or professional audio equipment.
What if the 3.5mm Audio Ports are not Color Coded?
Nowadays, most motherboard manufacturers are making their boards to improve the looks and aesthetics of the PC. As a result, some motherboards don’t have the regular color coded 3.5mm jacks. Instead, you will find them blacked out or in other colors to match the overall build of the motherboard.
How to find out the ports if all of them are black in color? If you have the motherboard’s user manual, then look in there. Usually, motherboard manufacturers describe all the ports on the motherboard in the manual to help new PC builders. Sometimes, even if all the motherboard audio ports are black in color, there will be a silkscreen (white paint) near each port describing the name or its symbol.
Conclusion
Audio plays an important role in modern computers. Whether you are using high-quality headphones or setting up a multi-channel surround sound system, you need a basic understanding of all the available audio ports on a motherboard. In this guide, we saw some commonly available motherboard ports including the famous 3.5mm Audio Ports as well as the popular S/PDIF Port. We also saw the significance of each port and what sort of speakers go into each of those ports. Comment * Name * Email * Website
Δ






![]()